Sample MCAT Question - Digestive System Anatomy & Function
Which of the following is not a function of the pancreas?
a) Produce insulin
b) Produce glucagon
c) Release digestive enzymes
d) Release bile
Get 1-on-1 MCAT Tutoring From a Specialist
With MCAT tutoring from MedSchoolCoach, we are committed to help you prepare, excel, and optimize your ideal score on the MCAT exam.
For each student we work with, we learn about their learning style, content knowledge, and goals. We match them with the most suitable tutor and conduct online sessions that make them feel as if they are in the classroom. Each session is recorded, plus with access to whiteboard notes. We focus on high-yield topics if you're pressed for time. If you have more time or high-score goals, we meticulously cover the entire MCAT syllabus.
Basic Function of the Digestive System
The general purpose of the human digestive system is to break down food particles for absorption. There are several ways the digestive system accomplishes this task. First, it mixes and reduces the size of ingested food through mechanical processes. Second, it secretes compounds and enzymes that help break down food and aid in the absorption of water. Lastly, it absorbs nutrients, electrolytes, and water directly from the intestinal lumen into the bloodstream.
Anatomy of the Digestive System
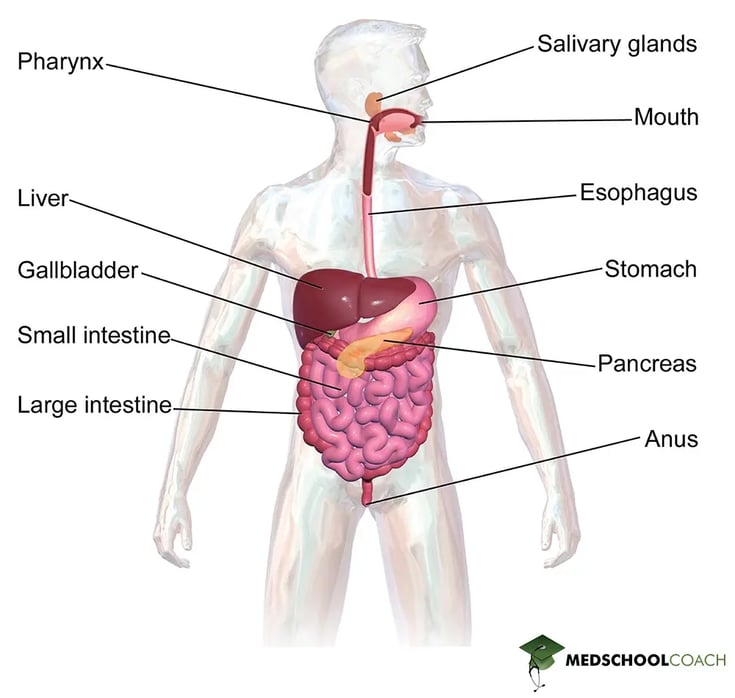
Figure 1 shows the anatomy of the digestive system. There are two main components – the alimentary canal, also called the gastrointestinal (GI) tract and the accessory organs. The GI tract is a tube that carries food throughout the body for digestion and absorption. It starts with the mouth and progresses to the esophagus, stomach, small intestines, large intestines, and ends with the anus.
The other digestive system component, the accessory organs, secrete compounds that aid in the digestion of food particles. These organs include the salivary glands, liver, pancreas, and gallbladder. The salivary glands produce saliva, which contains enzymes and proteins that start the chemical digestion process. The liver has many functions, including the production of bile, detoxification of harmful substances, the storage of glycogen, and gluconeogenesis. The pancreas has both exocrine and endocrine functions. The endocrine role of the pancreas is to produce the hormones insulin and glucagon, in order to regulate blood glucose concentrations. The exocrine role of the pancreas is to release digestive juices, including enzymes that break down molecules for absorption. Lastly, the gallbladder functions to store and release bile for digestion.
Explore More
MCAT Masterclass Chapters
Take a closer look at our entire MCAT Masterclass or explore our lessons below.
-
Endocrine vs Exocrine Glands
View Subject -
Digestive System Organs
View Subject -
Nervous System Structure & Function - MCAT Biology
View Subject -
Glycogenesis & Glycogen Regulation
View Subject -
The Lymphatic System
View Subject -
Types of Hormones
View Subject




