Sample MCAT Question - Neuron Structure
a) a synapse.
b) a dendrite.
c) an axon.
d) a soma.
Get 1-on-1 MCAT Tutoring From a Specialist
With MCAT tutoring from MedSchoolCoach, we are committed to help you prepare, excel, and optimize your ideal score on the MCAT exam.
For each student we work with, we learn about their learning style, content knowledge, and goals. We match them with the most suitable tutor and conduct online sessions that make them feel as if they are in the classroom. Each session is recorded, plus with access to whiteboard notes. We focus on high-yield topics if you're pressed for time. If you have more time or high-score goals, we meticulously cover the entire MCAT syllabus.
Neuron Structure
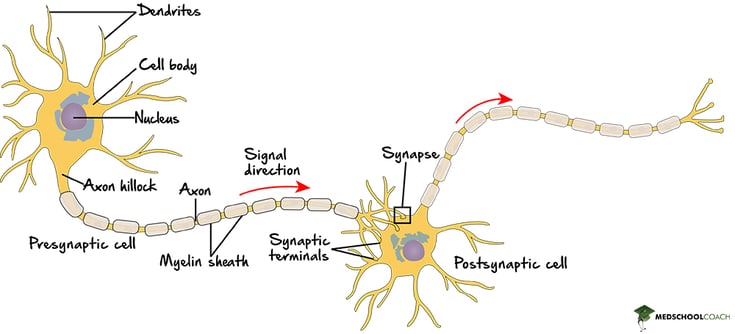
The neuron is made up of several essential components that are important to know for the MCAT exam. (These structures are illustrated in Figure 1.)
Dendrites & Soma
First, there is the cell body or the soma, which is the location of the cell nucleus as well as several other organelles. Emanating from the soma are dendrites, which are branched extensions of the soma that receive signals from other neurons. These signals are integrated in the soma and determine whether the cell will send its own signal by firing an action potential.
Axons, Myelin Sheaths, & Nodes of Ranvier
Next, there are the axons, which are long, slender projections of nerve fibers that send signals away from the soma. Most axons are very small in diameter, but they can reach great lengths. For instance, the motor neurons that control leg movement have axons that are up to one meter long.
Axons are covered by myelin sheaths. These sheaths insulate the axon and increase the efficiency of signal transduction. Without myelin sheaths, the signals neurons send along their axons, or action potentials, would not be as fast. The gaps between myelin sheaths are known as the Nodes of Ranvier. These are essential for the efficient and speedy transmission of the signal down the axon. When an action potential is transmitted, it does not travel the whole length of the axon, but appears to "jump" from node to node, thus ensuring faster signal transduction.
Synapses: Junctions Between Neurons
Lastly, the synapse is the junction between two neurons or, more accurately stated, the junction between the neuron and another cell. (Instead of synapsing onto another neuron, a neuron may synapse onto a muscle cell, gland, or organ.) The synapse is the site of signal propagation between two cells.
The neuron that transmits the signal is known as the presynaptic neuron, and the neuron which receives the signal is known as the postsynaptic neuron. In order for the signal to be propagated, the presynaptic neuron will release neurotransmitters that bind to receptors on the postsynaptic cell. Upon binding the neurotransmitters, the postsynaptic cell will undergo a reaction that may or may not result in the firing of an action potential. In order to transmit signals across long distances -- from the central nervous system to muscle fibers in the leg, say -- several neurons with multiple synapses are usually required.
Explore More
MCAT Masterclass Chapters
Take a closer look at our entire MCAT Masterclass or explore our lessons below.
-
Synapse
View Subject -
Oogenesis
View Subject -
Action Potentials, Refractory Period, and Summation
View Subject -
Resting Membrane Potential of Neurons
View Subject -
Reflex Arcs
View Subject -
Operant Conditioning: Reinforcement & Punishment- MCAT Psychology
View Subject




